- Home
- Symmetry Blog
- 5 Reasons to Embrace Augmented Reality in Manufacturing Operations
5 Reasons to Embrace Augmented Reality in Manufacturing Operations
About Jari Haiston

As a key player in immersive technologies, augmented reality (AR) has emerged as a game-changing tool in various industries and operations. More specifically, the integration of AR in manufacturing processes has shown remarkable potential to revolutionize the way products are designed, produced, and maintained.
What is Augmented Reality?
AR is a type of immersive technology that superimposes digital information, such as images, videos, graphics, or data, onto the real-world environment to enhance a user’s perception and interaction with their surroundings. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which creates entirely immersive digital environments, AR enhances real-world scenarios by incorporating digital elements to them. AR technology typically relies on devices like smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, and headsets, to overlay digital content onto the physical world.
Markets and Markets reports that the global AR market size was valued at $31.97 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach $88.4 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 31.5%. Moreover, Grandview Research reports that the industrial and manufacturing segment accounted for 24% of AR’s revenue share in 2022 (Figure 1). The projected growth surrounding AR in manufacturing industries can be attributed to its convenient abilities to assist organizations in error identification, downtime reduction, and more.
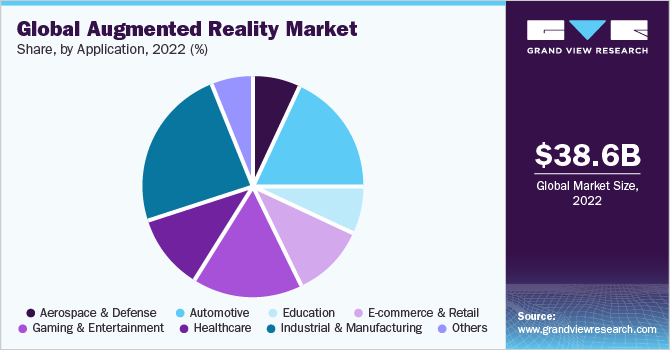
Source: Grandview Research
How Does Augmented Reality Work?
AR works through a combination of hardware devices, sensors, software algorithms, and digital content to blend virtual elements with the real-world environment. AR technology can:
- Sense the real world. AR devices use various sensors such as cameras, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and GPS to understand and track the user's physical environment. These sensors gather data about the user's location, orientation, and the objects around them.
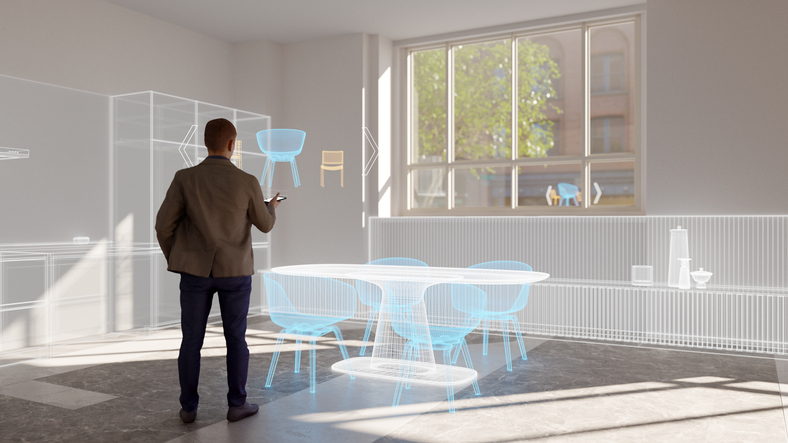

- Process and Recognize. The collected sensor data is processed by software algorithms to recognize and understand real-world elements, such as objects, surfaces, and locations.
- Overlay digital content. Once the software understands the environment, it superimposes digital content onto the user's view. This can include images, videos, 3D models, text, and more. The digital content is accurately positioned and scaled to align with real-world objects.
- Engage and Interact. Users can interact with the augmented elements, often through gestures, touchscreens, or voice commands. They can manipulate and manipulate the digital content as if it were a part of their physical environment.
Top 5 Reasons Manufacturers are Integrating Augmented Reality in Operations
AR has found numerous applications in manufacturing operations and is revolutionizing the way processes are executed, monitored, and optimized. The top five reasons manufacturers are rushing to integrate AR technology into their operations include:
- Enhanced Visualization and Design: Augmented Reality allows your team to visualize complex product designs in a three-dimensional, interactive space. This fosters better collaboration among design and engineering teams, leading to more informed decisions and streamlined development cycles. With AR, you can identify potential design flaws early on, reducing the risk of costly revisions down the line.
- Efficient Training and Onboarding: Training new employees on intricate manufacturing processes can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. AR simplifies this process by providing immersive, step-by-step visual instructions that guide operators through each task. This leads to faster training, reduced human error, and increased consistency in manufacturing procedures.
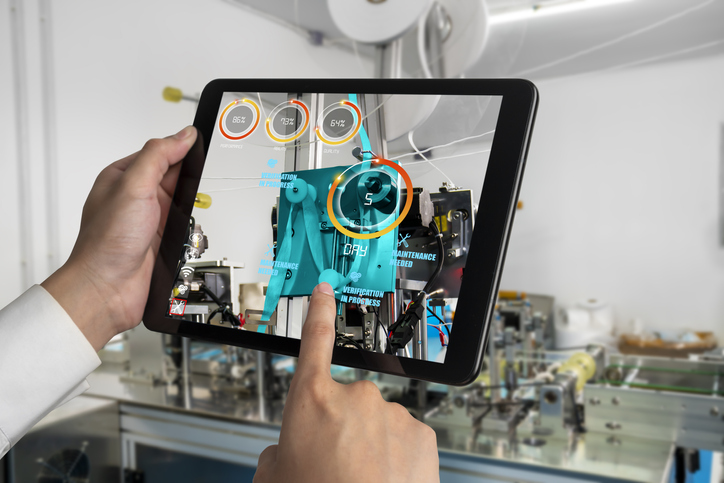
- Real-Time Data Overlay: One of the standout features of AR is its ability to overlay real-time data onto physical objects. By integrating IoT sensors and data analytics, AR-equipped devices can display critical information, such as machine performance, inventory levels, and quality metrics, directly onto the user's field of view. This empowers operators to make informed decisions on the spot, optimizing production processes and minimizing downtime.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Keeping manufacturing equipment in optimal condition is vital for maintaining productivity. AR simplifies maintenance tasks by providing technicians with visual, step-by-step guides for troubleshooting and repairs. Technicians can access digital manuals, diagnostic tools, and remote expert assistance, reducing equipment downtime and improving overall efficiency.
- Streamlined Quality Control: Augmented Reality enhances quality control by overlaying digital models onto physical products, enabling operators to compare the actual item against its design specifications in real time. This process ensures that products meet the highest quality standards and allows for swift identification of defects or deviations. As a result, you can achieve better product consistency and minimize waste.
Applications and Use Cases for AR in Manufacturing Operations
In addition to these five reasons to integrate AR innovation into your manufacturing processes, AR has a wide range of use cases and application in manufacturing, including:
- Assembly Guidance: AR provides step-by-step visual instructions overlaid onto physical products during assembly processes. This helps workers follow precise procedures and reduces errors in complex assembly tasks.

- Prototyping and Design: AR enables designers to visualize and interact with 3D prototypes in the real world. This enhances the design iteration process and fosters collaboration among design teams.
- Remote Assistance: Experts can provide remote assistance to on-site technicians by overlaying instructions, annotations, and diagrams onto their live view. This facilitates faster problem-solving and reduces travel costs.
- Spatial Planning: Manufacturers can use AR to visualize how equipment, machinery, and products will fit within a physical space before making layout decisions.
- Inventory Management: AR can assist in tracking inventory levels and locations using visual markers and data overlays. This streamlines stock management and reduces errors.
- Health and Safety Training: AR can simulate hazardous scenarios for training purposes, enabling workers to practice safety procedures in a controlled virtual environment.
- Digital Twin Interaction: AR allows operators to interact with digital representations of physical assets, exploring maintenance needs and simulations of potential operational changes.
How to Implement Augmented Reality in Your Manufacturing Operation
In conclusion, the integration of AR into manufacturing processes offers a multitude of advantages that can propel your company to new heights of efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness. From enhancing design and training to optimizing maintenance and quality control, AR brings a new dimension of possibilities to the manufacturing landscape. By embracing AR technology, you position your company at the forefront of Industry 4.0, ready to tackle the challenges and opportunities of the future with confidence.
If you’re interested in considering how you can implement AR innovation in your manufacturing operation, our knowledgeable team of Applications Engineers are available to simplify the seemingly complex world of immersive technologies. As experts in IoT, IIoT, and wireless technologies, our Applications Engineers are uniquely positioned to assist you in finding the ideal immersive technology to streamline your operations. For more information, contact Symmetry Electronics today!
