- Home
- Symmetry Blog
- Defining Additive Manufacturing
Defining Additive Manufacturing
Monday, November 7, 2022

From analog to digital, additive manufacturing (AM) is a technological advancement that is changing the game for manufacturers everywhere. Using computer-aided-design (CAD) software or 3D object scanners to direct hardware, additive manufacturing techniques deposit material, layer upon layer, in precise geometric patterns to create tangible objects. AM is commonly generalized to only include 3D printing or rapid prototyping processes, however, there are many different types of AM.
7 Types of Additive Manufacturing
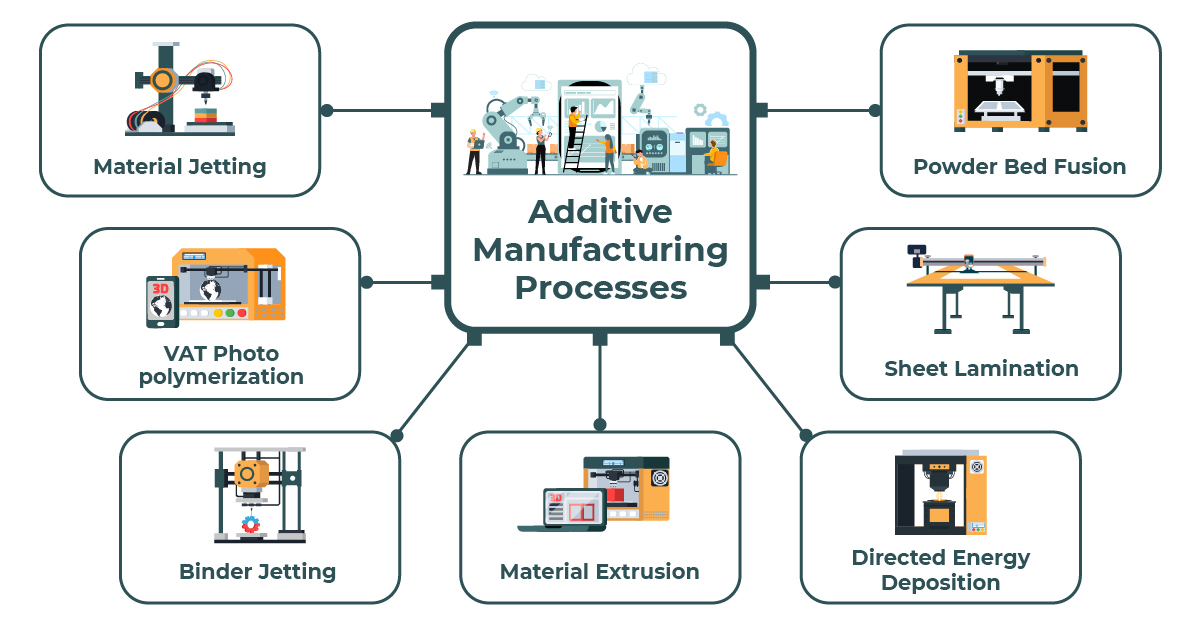
In comparison to traditional manufacturing, AM builds objects using a layer-based approach as opposed to eliminating excess from bulk objects through milling or other processes. There is a diverse range of AM processes, but many manufacturers focus on the seven most accessible forms of AM (Figure 1). The seven main types of additive manufacturing include:
1.Material Jetting
Similar to inkjet printers, material jetting uses droplets that are placed in selected patterns, layer by layer, to build an item. Every completed layer is cured by UV radiation.
2.Vat Photo Polymerization
Vat photo polymerization utilizes the chemical reaction between photopolymers or radiation curable resins, ultraviolet light, and oxygen to produce 3D objects. The three main subcategories of vat photo polymerization are Continuous Digital Light Processing, Digital Light Processing, and Stere lithography.
3.Binder Jetting
Binder jetting combines liquid binding agents with powdered material to deposit alternating layers of construction materials, bonding agent, and powder spreader to build a 3D object.
4.Material Extrusion
Patented in the 1980s by S. Scott Crump using Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), material extrusion utilizes thermoplastic filament that is fed through a heated nozzle. The filament is melted and placed layer by layer to produce a 3D object.
5.Powder Bed Fusion
One of the first types of industrial additive manufacturing ever used was laser sintering, a sub-category of powder bed fusion techniques. Powder bed fusion melts powdered material and fuses it via laser or electron beam to produce a 3D object. Other types of powder bed fusion processes include selective heat sintering, direct metal laser sintering, electron beam melting, selective laser melting, and laser sintering.
6.Sheet Lamination
Sheet lamination generally refers to processes that utilize ultrasonic additive manufacturing, laminated object manufacturing, and selective deposition lamination. Sheet lamination stacks laminate sheets of material to produce tangible items.
7.Directed Energy Deposition
Similar to welding processes, Directed Energy Deposition utilizes thermal energy to melt and fuse layers of material together to create a 3D object.
Harnessing The Advantages of Additive Manufacturing
Globe Newswire predicts that the value of the global additive manufacturing market will be valued at over $34 billion by 2028. AM’s growing popularity can be attributed to the benefits it provides. In the realm of the industrial internet of things (IIoT), additive manufacturing processes are essential tools that developers can use to eliminate supply chain complexity, streamline production, reduce waste, minimize prototyping costs, and limit pollution produced by manufacturing plants and warehouses.
As experts in everything IoT & IIoT, our team of experienced Applications Engineers are available to assist developers in selecting their ideal additive manufacturing process. Consultation is free and available throughout the entire design cycle. Contact Symmetry Electronics today!